Subcutaneous injections are used the preferred route for administration for some medications and vaccines. Previously, as a midwife I have memories of not only administering Heparin, post caesarean section, but also teaching women how to administer it themselves.
Subcutaneous injections are administered beneath the epidermis into the layer of fat and connective tissues. As the subcutaneous tissue does not have a rich blood supply, the drugs given are absorbed more slowly, than those given via the intramuscular route.
It is crucial to refer to your PGD for information regarding preferred administration route, as some medications can be given intramuscularly or subcutaneously.
Certain live attenuated vaccines such as MMR, varicella and yellow fever are administered by subcutaneous injection. Some inactive vaccines such as meningococcal polysaccharide are also recommended to be given via the subcutaneous route. It is imperative that you follow the PDG and only administer the medication as it states.
Suitable areas for administering a subcutaneous injection include, the upper outer area of the arm, the front and outer sides of the thighs, the abdomen) except for a 2inch area around the naval, the upper outer area of the buttocks.
The technique used to give a subcutaneous injection is as follows:
- Bunch the skin between the thumb and forefinger, this lifts the adiposed tissue from the muscle
- Hold the syringe between thumb and forefinger, insert the needle at a 45°angle and inject the solution slowly
- Once you have completed the injection, dispose of the needle into a sharps container
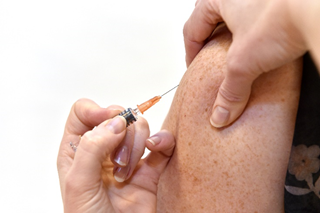
Patients with bleeding disorders and the flu vaccination, recent advice from Public Health England states that individuals may be vaccinated intramuscularly by a HCP who is familiar with the patients history and bleeding risk, a 23gauge (blue needle) should be used for vaccination, followed by firm pressure for at least 2 minutes, without rubbing.
Only certain flu vaccines are licenced to be administered by both intramuscular and subcutaneously, aTIV, Fluarix Tetra and Flucelvax Tera are NOT licenced for both, and can only be administered by intramuscular injection. https://www.gov.uk/government/collections/annual-flu-programme#2020-to-2021-flu-season
Remember, practice makes perfect, however, you must have consent from the person, prior to administering an injection!
Written by Lisa Humble (ECG Clinical Development Manager), Tuesday 15th September 2020
You can follow ECG Training at https://twitter.com/ECG_MK












